The Decarbonisation Imperative for Large Enterprises in Australia
As the world strives to reach decarbonisation goals, large enterprises have a crucial role to play. These companies, with extensive value chains, are significant contributors to carbon emissions, with industrial activity being the largest source of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. To reduce their carbon footprint, these enterprises must identify their emission hotspots, establish science-based targets for reducing emissions, and collaborate with supply chain partners to achieve these targets.
Why Decarbonisation is Critical for Enterprises in Australia
Enterprises that invest in decarbonisation by measuring and reducing their carbon emissions comprehensively, stand to gain a competitive advantage.
- More Stringent Regulation: Governments globally are implementing stricter emission regulations, and regulators are demanding greater accuracy in reporting and disclosures from businesses. Australia has committed to introducing a mandatory climate-related financial reporting regime. This would be more stringent than the existing financial reporting regime, in which Australian businesses are only recommended to report their climate-related performance in alignment with the Taskforce on Climate-related Financial Disclosure (TCFD). Businesses face the risk of penalties if they fail to comply with the upcoming mandatory climate-related financial reporting regime, but they can mitigate this risk by embarking on their decarbonisation journey with a trusted platform like Terrascope.
- Growing Awareness: Companies with a commitment to environmental responsibility are more likely to earn the trust and confidence of clients and customers. 50% of CFOs surveyed in the Deloitte European CFO survey cited improving reputation and winning customer trust as their primary motivations for decarbonising.
- Attracting Investments: Investors and banks are increasingly considering a company's carbon risk and sustainability track record before making investments.
- Reducing Costs: Decarbonisation can lead to cost savings through improved energy efficiency and reduced consumption. 38% of CFOs in the Deloitte survey cited cost savings as their primary motivation for decarbonising.
How can large enterprises begin their decarbonisation journey?
Industrial activity is one of the largest contributors to GHG emissions, accounting for 24% of the global total. Large enterprises are major contributors to these emissions, with the bulk coming from partners, suppliers, and customers in the value chain. These are known as Scope 3 emissions.
The Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP) reports that over 90% of a company’s emissions in agriculture commodities and 80% in the food and beverage industry come from Scope 3 emissions, while almost 100% of emissions in the financial services sector are Scope 3.
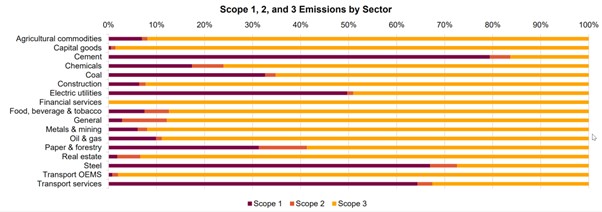
(Source: CDP)
To commence their decarbonisation journey, it's crucial for companies to identify the activities that contribute the most to their carbon emissions. The GHG Protocol has 15 categories of Scope 3 emissions that cover both downstream and upstream activities of a company. The activities that contribute the most to Scope 3 emissions will vary by sector, such as purchased goods and services accounting for 63.35% of total emissions in the agricultural commodities industry and use of sold products accounting for almost 90% in the capital goods sector.
Identifying these emission hotspots is a critical first step towards decarbonising operations across the value chain.
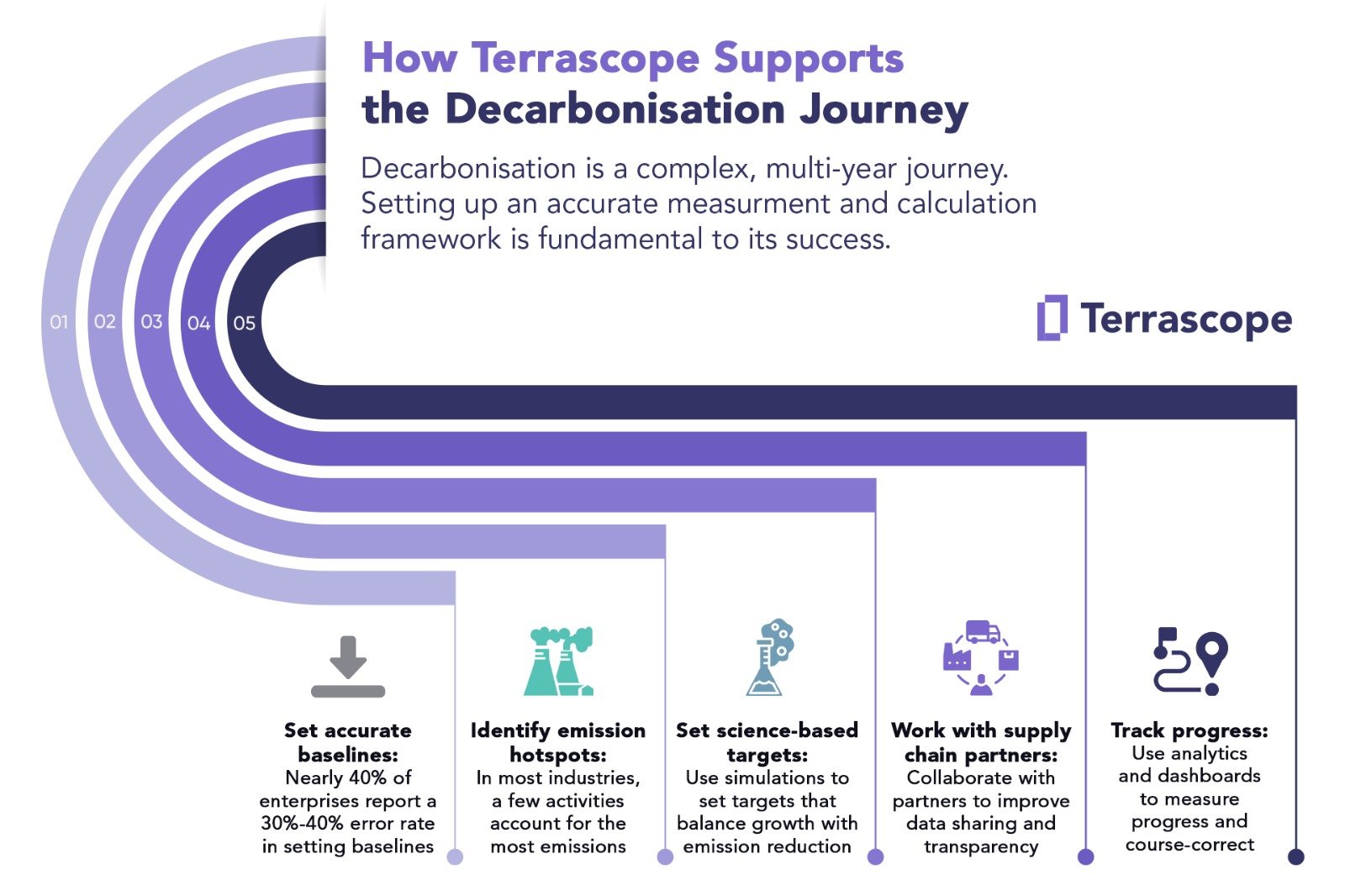
The Key Steps in the Decarbonisation Journey for Large Enterprises:
Step 1: Set Accurate Baselines Setting the right baselines is crucial for a successful decarbonisation journey. Research from the Boston Consulting Group (BCG) has found that a significant number of companies experience a 30-40% error rate in setting baselines due to data quality issues. Incorrect baselines can result in unrealistic reduction targets, and flawed disclosures, exposing companies to the risk of fines. Measuring emissions, particularly Scope 3 emissions, is a challenging task and requires accurate and standardised data from across the supply chain. Companies must work with their partners and suppliers to share better quality data and standardise disclosures, and consider using technology platforms to consolidate and standardise data collection.
Step 2: Identify Emission Hotspots In most industries, a few activities contribute to a majority of the emissions. In the chemicals sector, for example, upstream activities like purchased goods and services contribute almost 44% of emissions; in the construction sector, purchased goods and services account for nearly 30%, but a downstream activity like the use of sold products contributes 49% (Source: CDP). Similarly, some suppliers or regions may be greater contributors to Scope 3 emissions than others. Enterprises need to identify the emission hotspots and direct their reduction initiatives to areas that may yield the best results.
Step 3: Set Science-Based Reduction Targets The Science-Based Targets Initiative (SBTI) provides a pathway for reducing GHG emissions. To set realistic targets, enterprises must have a robust measurement framework in place and be able to accurately analyse scenarios and their outcomes. Emission reduction is a gradual process, involving intricate analysis and calculations to achieve both business growth and a reduction in carbon footprint.
Step 4: Work with Partners and Suppliers A significant portion of a company's emissions comes from their value chain, so they must support partners and suppliers in their decarbonisation journey. Encouraging partners to collect and share data, adopt robust accounting and disclosure standards, and re-evaluate procurement policies can be a good starting point.
Step 5: Track Progress Decarbonisation is a long, multi-year journey, and tracking progress is essential to stay on course. Companies must have the ability to access dashboards with advanced analytics and visualisation tools to gain actionable insights on their emission reduction measures.
How Terrascope Can Assist Your Journey to Decarbonisation
Terrascope is a comprehensive, smart carbon measurement and management platform designed for enterprises. It leverages data science, machine learning, and sustainability expertise to provide the data, analytics, and digital tools necessary to help large companies decarbonise their operations and supply chains.
Our platform has been onboarded globally by companies across various industries, including Agriculture, Food and Beverages, Industrial Manufacturing, Luxury, Transportation, and the Public Sector.
If your company is committed to reducing its carbon footprint, connect with our emissions experts today. Our team has extensive experience working with numerous large enterprises on their emissions measurement and management needs.
